Why Hydrogen?
The urgency of addressing climate change and achieving the UN's Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) is undeniable. Our reliance on fossil fuels has led to environmental degradation, economic instability, and threats to human health. Transitioning to a clean energy future is crucial, and hydrogen offers a promising pathway.
Why Hydrogen?
Hydrogen is a versatile energy carrier that can be produced from diverse sources, including renewables, nuclear, and fossil fuels with carbon capture. It can be used in various sectors, contributing to multiple SDGs, including, but not limited to:
- SDG 7 (Affordable and Clean Energy): Hydrogen can decarbonize electricity generation, transportation, and industrial processes, providing clean and affordable energy access.
- SDG 9 (Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure): Hydrogen fuels innovation in sectors like transportation, manufacturing, and building, supporting sustainable industrial development.
- SDG 11 (Sustainable Cities and Communities): Hydrogen-powered vehicles and infrastructure contribute to cleaner air and healthier urban environments.
- SDG 13 (Climate Action): Replacing fossil fuels with hydrogen significantly reduces greenhouse gas emissions, mitigating climate change.
Hydrogen's Applications:
Hydrogen's versatility is evident in its wide range of applications, including:
- Transportation: Fuel cell vehicles, hydrogen-powered trains, and aviation.
- Industry: Producing ammonia for fertilizers, upgrading bitumen, and metallurgical processes.
- Power Generation: Clean electricity generation and energy storage.
- Buildings: Heating and power for residential and commercial buildings.
The growing hydrogen market presents significant economic opportunities. By investing in hydrogen technologies, we can foster innovation, create jobs, and transition to a sustainable energy future."
By adding "including, but not limited to," we acknowledge the potential for hydrogen to contribute to a wider range of SDGs, further strengthening the argument for its importance in a sustainable future.
Hydrogen 1.0: A New Era in Clean Energy
The concept of Hydrogen 1.0 represents a transformative shift toward a hydrogen-based society, addressing global energy, environmental, and economic challenges. It emphasizes the integration of hydrogen energy solutions into various sectors to achieve sustainability.
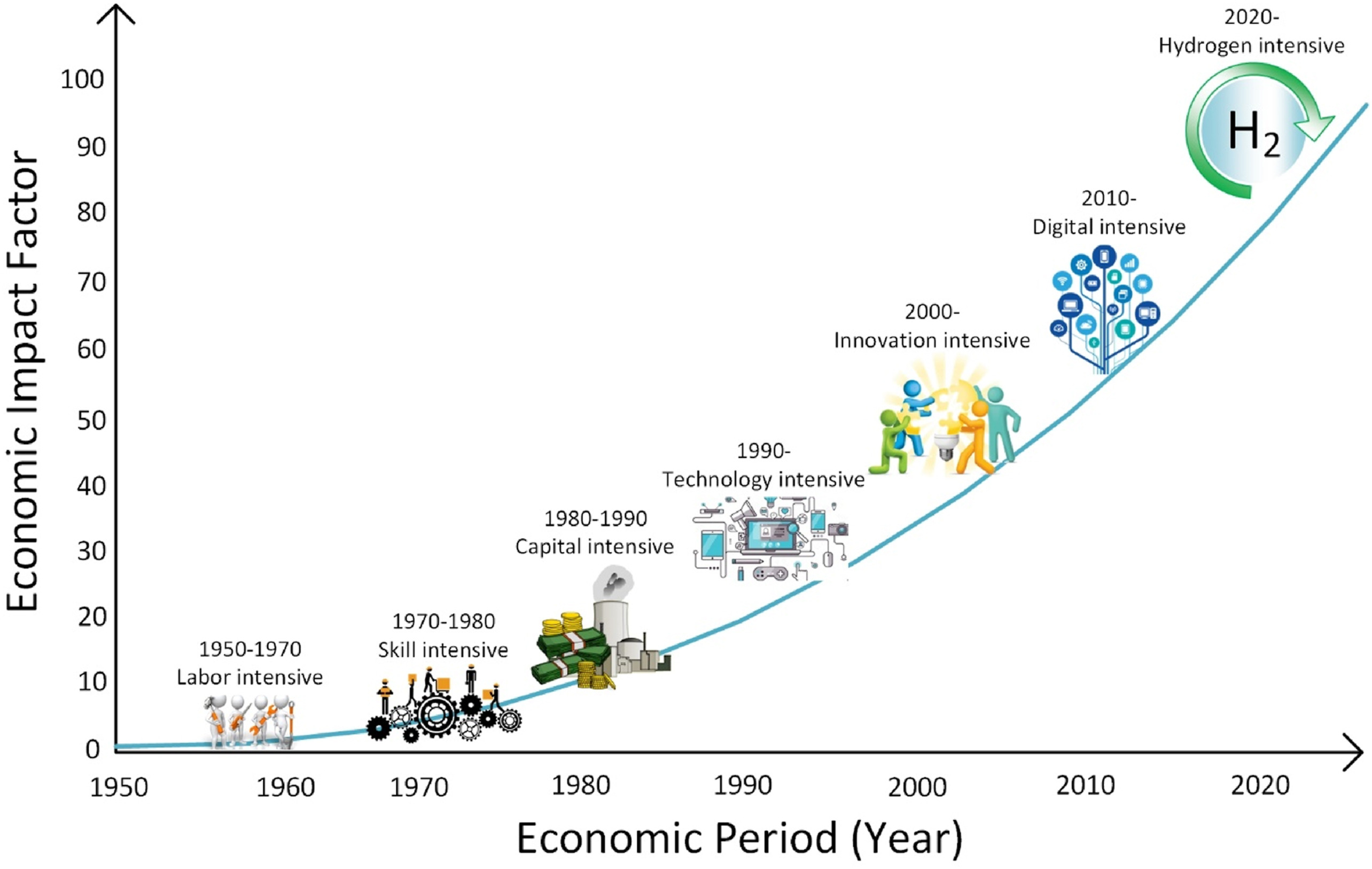
Figure below illustrates the economic evolution since the 1950s, highlighting key periods such as labor-intensive, capital-intensive, technology-driven, and innovation-driven economies. The latest shift—marked by digitalization and the transition to hydrogen—positions clean hydrogen as a central element for economic growth and sustainability.
Key Requirements for Hydrogen 1.0
Figure below presents the six essential domains for the Hydrogen 1.0 framework:
- Better Design: Innovative hydrogen systems from production to distribution.
- Better Efficiency: Optimization of energy and exergy efficiency.
- Better Resource Use: Sustainable utilization of natural and human resources.
- Better Environment: Reducing carbon emissions and fostering a green economy.
- Better Energy Security: Hydrogen as a resilient energy source.
- Better Economy: Economic feasibility and competitiveness of hydrogen-based solutions.

Through technological advancements, innovation, and digitalization, Hydrogen 1.0 aims to establish a cleaner, more sustainable energy future.